Every business generates geographic data, including customer addresses, delivery routes, and competitor locations. But most only use this information for record-keeping, leaving valuable insights untouched.
Location intelligence provides new ways to use geographic data. It organizes, coordinates, and converts zip codes and addresses into usable information for decision-making.
For example, a retail chain can strategically map its customers, traffic patterns, and competitors to choose the optimal location for a new store. Similarly, a logistics company can maximize efficiency by viewing all its delivery routes and real-time conditions, thus avoiding wasted fuel. In both cases, the data companies have already become a powerful asset when used in this way.
IBM emphasizes that location intelligence uncovers valuable insights from geospatial data. While that’s true, the real advantage for your business is the ability to make smarter, faster decisions with geographic context as your guide.
Table of Contents
Your existing data starts the process. Customer records list addresses. Sales figures link to territories. Inventory levels are tied to warehouses. Service calls reference specific locations. This information already exists in your systems, often scattered across multiple databases and spreadsheets that never communicate with each other.
Location intelligence platforms empower you to unite scattered data and visualize it in a way spreadsheets never could. Patterns jump out, such as clusters of high-value customers, gaps in your service network, and the direct impact of store placement on sales, which are now apparent for decisive action.
Mapping is just the beginning with location intelligence. Once you analyze the data, you unlock new opportunities: target high-value customers, balance resources, optimize routes, leverage heat maps to identify high-activity zones, and make location-based decisions that give you an edge over the competition.
Location intelligence tools are more powerful than ever. With cloud-based solutions capturing over 63% of the market and growing rapidly, businesses can now gain robust geographic analysis without specialized staff or infrastructure. This is your chance to join a technology-driven movement and leap ahead of competitors.
Market Growth Reports reveal a compelling truth: in 2024, more than 72% of Fortune 1000 companies relied on location-based insights to stay ahead. Companies with mature geospatial strategies consistently outperform those still lagging. This is clear evidence that spatial data is now essential for top-tier decision-making.
Based on feedback from over 500 executives spanning financial services, retail, logistics, real estate, and travel industries, the results are clear: leaders who embrace location intelligence report up to 2x improvements in customer satisfaction, sales, and operational efficiency.
Doubling operating efficiency requires a different approach to decision-making, according to the study.
Retail and consumer goods companies led the way in using location intelligence, capturing 24.54% of the market in 2024, according to Mordor Intelligence. Store location stands as one of the biggest factors in a store’s success.
McDonald’s Germany provides a case study in systematic location analysis. With a strong franchise network of over 1,400 sites and a commitment to continuous growth, the company constantly seeks new locations that meet high standards for accessibility, visibility, and guest potential.
The company calculates guest potential for locations based on demographic data and the frequency of typical mealtimes, as well as travel time analysis to reach a restaurant.
Each restaurant needs excellent connections and easy accessibility by car, on foot, or by bicycle. The company considers visibility from the main road very important. If visibility exists, customers can also approach the restaurant from a side street.
Warby Parker uses a similar strategy but with different measures. The company has carefully expanded its physical stores, opening about 40 each year from 2022 to 2024. It plans to open 45 more in 2025, bringing the total to 300 locations, including Brookfield Place.
Warby Parker continues to enter new and existing markets where it sees high online penetration, whether that’s malls, streetfronts, or lifestyle, hybrid, and grocery-anchored centers, with a focus on meeting customers where they are.
These examples show that geographic analysis yields more informed site choices than intuition alone.
Delivery operations face routing challenges every day. Each driver must find the most efficient path through multiple stops, accounting for traffic, time windows, and vehicle capacity. Manual planning cannot optimize all these factors for many routes at once.
Research from xmap.ai found that after one major retailer switched to dynamic route planning, on-time delivery reliability reached 92% while average delivery times fell by more than a third. The same analysis showed that mapping return drop-off points and transportation routes allowed retailers to identify patterns and streamline processes, cutting related costs by 28%.
Maptive’s route-optimization features yield similar results. According to Millennial Magazine, tests by logistics teams showed routing errors decreased by approximately 22%, while fuel costs in pilot studies fell as much as 15%.
A field service company reported an 18% drop in fuel costs and a 22% increase in completed service calls after adopting the platform. A logistics firm processed thousands of routes in seconds and reduced holiday shipping delays by over 40%.
Efficiency improvements from cost savings and increased service calls directly benefit business operations. Investment in location intelligence can provide ongoing returns.

Property values depend on nearby amenities, schools, transportation, and other properties. Geographic data clarifies and measures these variables.
Real estate professionals use location intelligence to analyze market trends and property valuations, taking into account factors such as proximity to amenities, schools, and transportation options.
The same tools retailers use to select stores can help real estate investors identify undervalued properties. Route optimization can help property managers plan maintenance tasks. Geographic analysis helps real estate by providing location-based insights.
Supply chain managers constantly decide where to keep inventory, how to route shipments, and when to change the network. Location intelligence provides the geographic information needed for these choices.
Organizations can use location intelligence to design and optimize supply chain networks, run simulations to identify the most suitable location for warehouses and distribution hubs, generate optimal routes, analyze demand patterns, and minimize costs.
Unacast notes that integrating location intelligence into supply chain management enables companies to streamline logistics by analyzing traffic patterns and delivery routes, thereby reducing transportation costs and improving delivery times.
Supply chain disruptions highlighted specific weaknesses in logistics networks. Geographic tools can help identify risks in advance. Mapping suppliers reveals concentrated risks, visualizing networks shows gaps, and simulations test network resilience.
Traditional marketing segmentation only scratches the surface. With location intelligence, you supercharge marketing efforts, unleashing personalized campaigns that target customers where they are for maximum impact.
Analyzing location data enables businesses to gain deeper insight into customer behavior and preferences. They can create personalized marketing strategies and tailored services that resonate with specific demographics. Retailers identify high-traffic areas and ensure products and promotions reach possible customers.
Grand View Research reports that sales and marketing optimization generated nearly $4.88 billion in revenue in 2024. That spending reflects the proven returns from location-based marketing approaches.
Geographic segmentation shows patterns that other methods miss. Urban and suburban customers may act differently even if their demographics are similar. How close a store is affects how often people shop, and commute patterns influence shopping times and places. Location intelligence makes these trends easy to see and use.
The platform you choose determines your competitive edge. Avoid complicated tools that slow you down or basic tools that constrain potential. Select a solution that delivers both power and simplicity, giving you truly actionable geographic insights.
Maptive proves that mapping software can make your life easier without sacrificing power. With robust features like auto-updating maps, seamless integration, and enterprise-class security, you gain complete control and confidence as you capitalize on location intelligence.
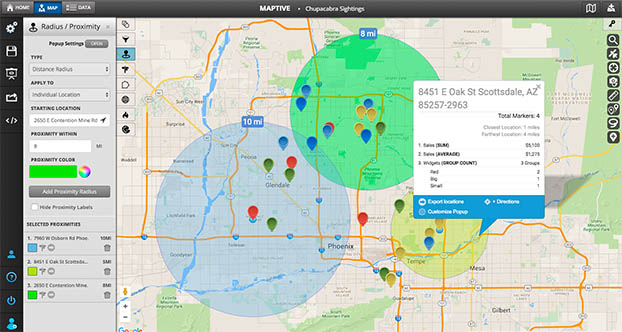
Our platform lets you upload unlimited data without delays, handling over 20,000 data points per map in real time. It can also be used for sales territory planning, customer mapping, route planning, and competitive analysis.
Users can map businesses, suppliers, and competitors to help choose sites. The distance matrix calculator finds distances between points for assigning sales reps, spotting nearby competitors, and planning supply chains.
Location intelligence is widely used as a business tool. Companies using geographic insights may improve operations, customer engagement, and identify new opportunities.
Maptive offers location intelligence through an easy-to-use, cloud-based platform powered by Google’s mapping technology. The platform turns raw data into valuable geographic insights without needing coding or special training.
Try our software free for 10 days before you buy. No credit card is needed, and there are no hidden fees. Use our mapping tools to find new opportunities in your data today.
Fred Metterhausen is a Chicago based computer programmer, and product owner of the current version of Maptive. He has over 15 years of experience developing mapping applications as a freelance developer, including 12 with Maptive. He has seen how thousands of companies have used mapping to optimize various aspects of their workflow.
