
A sales manager with 400 customer addresses needs to quickly identify how many are within 25 miles of a new warehouse. Rather than calculating each distance manually, which is time-consuming. She uses radius mapping to see the result instantly. This tool highlights nearby locations, providing businesses with clear, actionable insights in seconds.
Radius mapping lets you draw a circle, called a radius, around any spot on a map to see what’s included within that area. Choose a location and set your preferred distance; the software generates a circle for your analysis.
Businesses use radius mapping for territory planning, site selection, delivery zones, and customer segmentation. The main question is always the same: what is within a certain distance from this location?
Table of Contents
Start with a central point, such as a store or distribution center, and set a radius. The software draws a circle, highlighting which data points are inside.
Many tools let you add multiple circles at once. For example, you can create 5, 10, and 25-mile circles around a location to compare coverage at different distances. This approach helps you see how your reach expands from a central point.
Add your own business data to radius maps to reveal immediate visual patterns. This makes it easy to identify customer density and market coverage gaps. The main strength: complex data becomes instantly clear, ensuring decisions are based on accessible insight.
Retailers often use radius mapping to choose new store locations. Before opening, they look at population density, household income, and where their current customers live within the area they want to serve.
According to Grand View Research, the sales and marketing optimization segment represented 23% of the location intelligence market in 2024. Much of this activity involves geographic analysis tools, such as radius mapping.
Logistics and delivery teams use radius mapping to set service zones and plan routes. Companies draw circles around distribution centers to see which customers they can serve well and where they might need more locations.
Field sales teams use radius mapping to balance territories. When each salesperson has a designated area, managers use radius mapping to assign accounts fairly and reduce travel time. Sales organizations that thoughtfully design and optimize sales territories can realize 10% to 20% increases in sales productivity, according to Alexander Group. Companies using territory mapping tools report cost reductions of up to 25%.
Spreadsheets and maps can hold the same information, but we understand them differently. A list of addresses is just data, but seeing them on a map with radius circles shows relationships. Kissmetrics reports that high-quality infographics are 30 times more likely to be read than plain text.
Location analytics is growing. Grand View Research estimated the global location intelligence market at $21.21 billion in 2024 and expects it to reach $53.62 billion by 2030. In 2024, the U.S. generated $5.36 billion in location intelligence revenue. Many organizations use geographic visualization tools for faster decision-making.
Retail foot traffic increased by 0.4% in 2024, according to Placer.ai, indicating that people still visit stores. But rents in busy areas are now 20% to 40% higher than before the pandemic. This makes accurate location analysis more critical than ever. Businesses need to be sure when choosing sites or setting service areas.
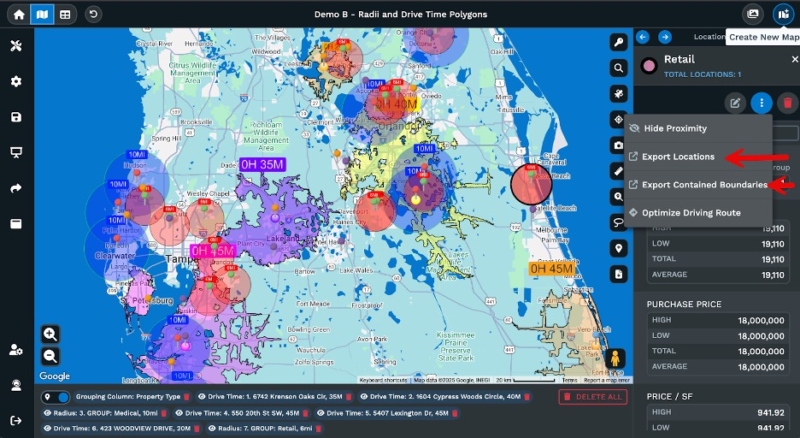
Radius mapping uses straight-line distance to draw circles. A 10-mile radius covers everything within 10 miles of the center, no matter the roads or traffic. This method is suitable for broad market analysis and early location screening.
Drive time mapping is different. It measures how long it takes to drive somewhere, not just the distance. A 30-minute drive-time area can appear uneven because it accounts for highways, traffic, and road layouts. In some directions, you might reach 25 miles in 30 minutes, while in others, you only get eight miles.
Both methods are helpful. Radius mapping provides quick, standardized measurements for comparing locations or defining rough service areas. Drive time mapping is more effective when travel time matters, such as for deliveries or service calls. Many businesses use both at different points in their analysis.
Today, getting started with radius mapping is simple and central to an effective business strategy. Growing access to cloud-based mapping tools means any business can now unlock quick location insight; no special setup needed.
Modern radius mapping tools work with your business data. Upload a spreadsheet of addresses, and the software plots them on a map. Draw circles around any point to see which locations fall within each zone, all within minutes.
The best tools also offer demographic data. You can add census data to your radius maps to view details such as age, income, and population density for each zone. For retail site selection, these layers help you find areas with the right customer profile.
When choosing a radius mapping tool, ease of use is key. If the software is too complex to learn, people won’t use it. Look for tools that let you upload data and quickly create maps without special skills.
It’s also vital that your mapping tool integrates well with your current data sources, such as CRM systems, spreadsheets, and other databases. The easier it is to get your data onto a map, the more likely your team will use the tool.
Map quality affects both accuracy and usability. Platforms built on professional-grade mapping infrastructure deliver better performance, more accurate geocoding, and a smoother user interface. Maptive uses mapping technology that offers global coverage and reliable performance familiar to many users.
With Maptive’s radius mapping tool, you can draw circles in miles or kilometers from any point on your map. Add as many circles as you need and quickly analyze your location data. The platform shows where your data points are, how far apart they are, and how many fall within each distance range.
Beyond basic radius mapping, our platform gives you access to U.S. and Canadian census data for deeper research. You can set up sales territories by ZIP code, state, or other boundaries, using built-in data like population, age, and income. This helps you target the right areas and keep territories balanced for sales and marketing.
Many users find Maptive helpful for location planning and market research. The drive-time radius feature supports site selection, and the platform is used in logistics, project tracking, and scheduling.
Try a free 10-day trial, no credit card required. Explore the features, draw radius circles, and view your business data in new ways. Request a demo to see how the mapping tools can improve your operations and location decisions.
Brad Crisp is the CEO at Maptive.com, based in Denver, CO and born in San Francisco, CA. He has extensive experience in Business Mapping, GIS, Data Visualization, Mapping Data Analytics and all forms of software development. His career includes Software Development and Venture Capital dating back to 1998 at businesses like Maptive, GlobalMojo (now Giving Assistant), KPG Ventures, Loopnet, NextCard, and Banking.
