Spatial analysis examines geographic relationships and location patterns through computational methods that combine geographic information systems with artificial intelligence. Organizations apply these techniques to understand how physical locations, distances, and spatial arrangements affect business operations, environmental conditions, and social patterns. The field merges mapping technologies with predictive analytics to process data from satellites, sensors, and mobile devices.
Table of Contents
The geospatial analytics market reached USD 114.32 billion in 2024 and will grow to USD 226.53 billion by 2030, expanding at 11.3% annually through this period. This growth stems from organizations recognizing spatial intelligence as essential infrastructure for their operations. Companies invest in these capabilities to improve operational efficiency, reduce risks, and make better strategic decisions through automated feature extraction and predictive modeling.
Artificial intelligence transforms geographic information systems from static mapping tools into adaptive platforms that predict future conditions. Machine learning models examine historical spatial patterns and correlate them with real-time data feeds to forecast upcoming events. These systems process spatial data through deep learning and computer vision to generate automated geospatial insights that would take human analysts weeks to produce manually.
Cities worldwide implement AI-powered GIS platforms to monitor traffic patterns, manage utility networks, and coordinate emergency responses. Singapore’s Smart Nation 2.0 initiative demonstrates advanced geospatial implementation through Virtual Singapore, a three-dimensional city model that functions as the city’s twin. The SGD 73 million project, led by the National Research Foundation, integrates geometric and image data from public agencies with real-time sensor feeds deployed throughout the city.
The Virtual Singapore platform combines topographical data from the 3D National Mapping project with information from existing geospatial platforms including OneMap, People Hub, and Business Hub. This integration enables planners to assess infrastructure projects and their effects on traffic patterns without manual analysis. Smart traffic management systems use real-time data to adjust traffic flow dynamically, reducing congestion and improving commute times across the city.
Farmers employ AI-driven GIS tools to analyze soil quality, weather patterns, and crop health for yield predictions. These precision agriculture technologies monitor soil conditions, crop performance, irrigation patterns, and pest detection through drones, satellite imagery, and ground sensors. Agricultural businesses gain real-time insights that reduce waste and improve yield forecasts while cutting water consumption through intelligent irrigation scheduling.
An AI-powered GIS platform enables farmers to anticipate drought conditions and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly, conserving resources while maximizing crop output. The surface and field analytics segment continues growing as more agricultural operations adopt these technologies for monitoring and optimization. Mobile signal data provides 90 percent precision for tracking equipment movement patterns, enabling dynamic response to changing field conditions.
Machine learning models process satellite imagery to detect changes in land use, vegetation coverage, and urban expansion patterns. Conservation organizations employ GeoAI systems to monitor deforestation and protect endangered species habitats through automated detection of illegal logging activities. These systems enable faster enforcement actions by automatically identifying unauthorized activities in protected areas.
Researchers applied ANP and ANN models combined with GIS technology to identify flood-prone areas using field surveys, historical flood data, and satellite imagery. After analyzing 226 flood locations separated into training and validation datasets, the ANP model classified approximately 10% of studied areas as having high flood susceptibility, while the ANN model identified 14% as very high risk zones. These assessments help communities prepare for and prevent flood damage through better planning and resource allocation.
AT&T utilized climate data and geospatial analysis to map potential flooding risks to its United States infrastructure through 2050. The company’s geospatial AI systems identified facilities and supply chains vulnerable to coastal flooding, producing detailed risk assessments that other organizations now use for their own vulnerability evaluations. This proactive approach helps companies protect critical infrastructure before disasters occur.
The Bavarian State Ministry of Housing, Building, and Transport tested an artificial intelligence system for assessing road conditions on a major German highway. The predictive analysis uses geospatial AI to analyze images and identify early signs of road wear, determining exactly when and where to schedule maintenance before major repairs become necessary. The project demonstrated that these approaches can forecast changing road conditions accurately, reducing maintenance costs and improving road safety.
Maptive provides spatial analysis capabilities for business applications without requiring coding expertise, while supporting analytical functions for large-scale operations. The platform processes up to 100,000 locations simultaneously, enabling comprehensive spatial analysis for organizations of various sizes. With the release of Maptive iQ, new features support advanced spatial analysis through enhanced drive-time polygon tools that calculate multi-hour service areas with improved accuracy.
The drive-time polygon feature now uses 300 percent more calculation points than earlier versions, producing smooth and detailed polygon edges. Users can plan drive times up to four hours with better accuracy, and an update scheduled for late 2025 will enable eight-hour windows. These capabilities support precise delivery planning, territory optimization, and customer accessibility analysis for logistics and sales operations.
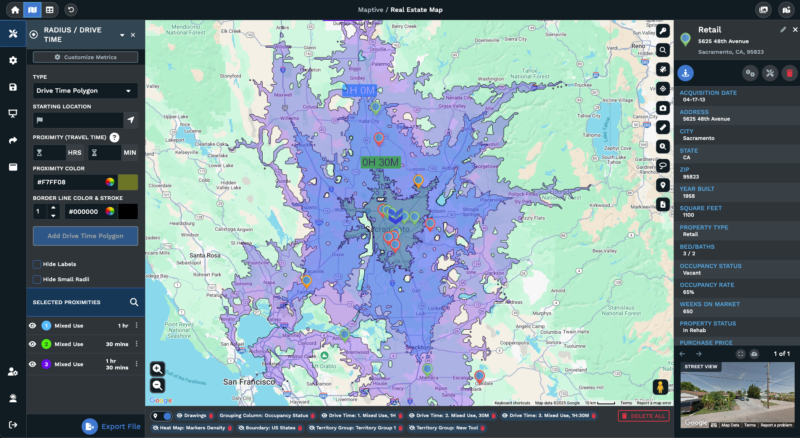
Maptive unified its Boundary and Territory tools to provide greater flexibility for map management and customization. Users can convert territories created from boundaries into polygons for seamless adjustments and reconfigurations. Adding or removing boundaries becomes straightforward, enabling region creation based on states, counties, or previously saved data patterns.
The platform expanded demographic data options to include population, median income, and additional metrics in radius popups, drive-time polygons, boundaries, and territories. Heat maps and demographic overlays showing household income, population density, or shopping trends can be added to any geographic area. User testing shows that these overlays provide deeper insights into sales region performance and potential new location success rates.
Maptive iQ includes route optimization features for delivery operations that check all possible delivery routes before selecting the fastest and most cost-effective option. The program considers traffic delays, standard closures, and time of day to create realistic and achievable plans while maintaining accurate customer time windows. Tests by logistics teams show routing errors decrease by approximately 22%, while fuel costs in pilot studies fell as much as 15%.
Fleet management systems process millions of location updates each day, optimizing routes dynamically based on current traffic conditions and delivery priorities. Transportation companies leverage this real-time spatial intelligence to reduce operational costs while improving service reliability. The combination of predictive analytics and real-time data enables proactive route adjustments before delays occur.
AI automates repetitive tasks including data cleaning, spatial analysis, and mapping updates for disaster management. Automated GIS workflows generate evacuation maps in minutes rather than hours, enabling faster emergency responses. First responders utilize dynamic routing, resource allocation maps, and population density analysis for effective crisis management during disasters.
The disaster risk reduction and management segment continues growing due to increasing demand for early warning systems and real-time monitoring capabilities. Spatial analysis enables forecasting of high-risk areas for floods or wildfires based on weather patterns, topography, and historical occurrences. This information allows timely evacuation warnings and proper resource allocation before disasters strike.
Epidemiological mapping enhances public health response capabilities through sophisticated spatial modeling techniques. Disease spread patterns, vaccination coverage analysis, and healthcare resource optimization rely on geographic data to identify trends and allocate resources effectively. Public health officials use these tools to track outbreak patterns and predict future spread based on population movement and environmental factors.
The geospatial analytics market for healthcare applications will reach USD 174.44 billion by 2030, growing at 12.72% annually from the current USD 95.84 billion valuation in 2025. This expansion reflects increasing demand for location-based insights in healthcare planning and disease prevention. Spatial intelligence helps healthcare systems optimize facility locations and improve patient access to care.
The network and location analytics segment grows rapidly due to increased adoption of location-based services in retail, transportation, telecommunications, and urban planning sectors. Businesses leverage location analytics to understand customer behavior, foot traffic patterns, and regional preferences for targeted marketing, site selection, and personalized service delivery.
Customer catchment analysis, competitor proximity mapping, and demographic profiling guide expansion strategies and marketing investments for retail chains. Organizations analyze spatial data to identify underserved markets and optimize store locations based on population density and purchasing power. These insights reduce the risk of new location failures while maximizing return on investment.
Spatial modeling combines multiple data layers for carbon footprint mapping, renewable energy site selection, and climate impact assessments. Weather pattern analysis enables predictive modeling for agricultural planning and disaster preparedness across regions. Organizations use these capabilities to measure environmental impacts and plan mitigation strategies based on geographic factors.
Geospatial data encompasses satellite imagery, coordinates, and terrain information essential for urban planning, agriculture, and disaster response applications. Climate scientists analyze this data to track changes in temperature patterns, precipitation levels, and extreme weather frequency. These insights inform policy decisions and help communities prepare for climate-related challenges.
The Spatial Statistics 2025 conference scheduled for July 15-18 in Noordwijk, Netherlands, will focus on artificial intelligence applications in spatial analysis. The conference at NH Leeuwenhoorst will present developments in spatial statistics and their contributions to AI advancement. Topics include optimal data use, space-time prediction, object recognition and segmentation, and transferability in the presence of spatial and temporal correlations.
Organizations invest heavily in spatial intelligence training as they recognize competitive advantages from location-based insights. Professionals acquire skills in AI-powered GIS solutions to remain competitive in rapidly changing industries. Cloud-based platforms provide access to sophisticated spatial analysis capabilities through subscription models, eliminating infrastructure barriers for smaller organizations.
Three-dimensional mapping features planned for 2025 will enable architects and engineers to overlay site data or city features in 3D for improved urban project planning. Point cloud processing support will produce 3D mapping models with fine accuracy for volumetric analysis, underground infrastructure mapping, and vertical city planning applications. These advanced three-dimensional spatial intelligence capabilities will expand analysis possibilities across multiple industries.
Spatial analysis transforms raw location data into actionable intelligence by examining geographic relationships through advanced computational methods. The convergence of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and geographic information systems creates capabilities for solving complex spatial problems across industries. Organizations optimize operations, reduce risks, and identify opportunities through geographic understanding as location becomes fundamental context for business decision-making.
Brad Crisp is the CEO at Maptive.com, based in Denver, CO and born in San Francisco, CA. He has extensive experience in Business Mapping, GIS, Data Visualization, Mapping Data Analytics and all forms of software development. His career includes Software Development and Venture Capital dating back to 1998 at businesses like Maptive, GlobalMojo (now Giving Assistant), KPG Ventures, Loopnet, NextCard, and Banking.
