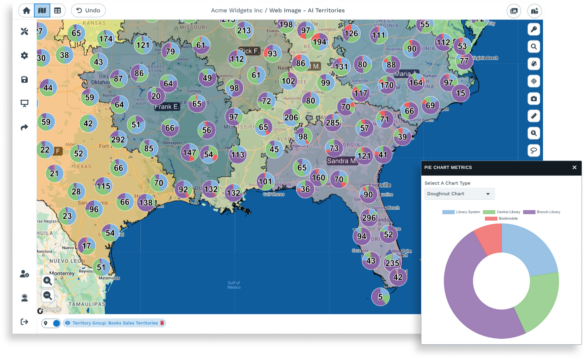
Map charts are indispensable tools for decoding information through a geographical lens, and are poised to play a bigger and bigger part in the location intelligence sector.
The demand for location-based insights is growing worldwide, according to industry research, with the global location intelligence market size valued at $18.52 billion in 2023 and projected to grow up to 15.6% from 2023 to 2030.
Map charts are the perfect answer to industry demands, as they solve the needs of analysts and decision-makers alike. They efficiently communicate intricate data patterns, trends, and relationships by harnessing a wealth of geospatial data.
Notably, the surge in availability of geospatial data as open data, driven by contributions from public and private organizations, has enabled users to access this valuable resource freely through open standards. This, in turn, has heightened the significance of map charts, making them the ideal tool to display demographic data, sales performance, and other location-dependent metrics.
This is also because, by their very nature, map charts accomplish so much more than traditional charts. They enhance understanding by connecting data points to real-world locations, making it easier for users to grasp spatial relationships. Plus, map charts facilitate better decision-making by providing a comprehensive view of regional variations, something that is becoming increasingly valuable as organizations look for richer insights from their data.
Table of Contents
By definition, a map chart is a visual representation of data that links information to specific geographic locations. Popular map chart types include:
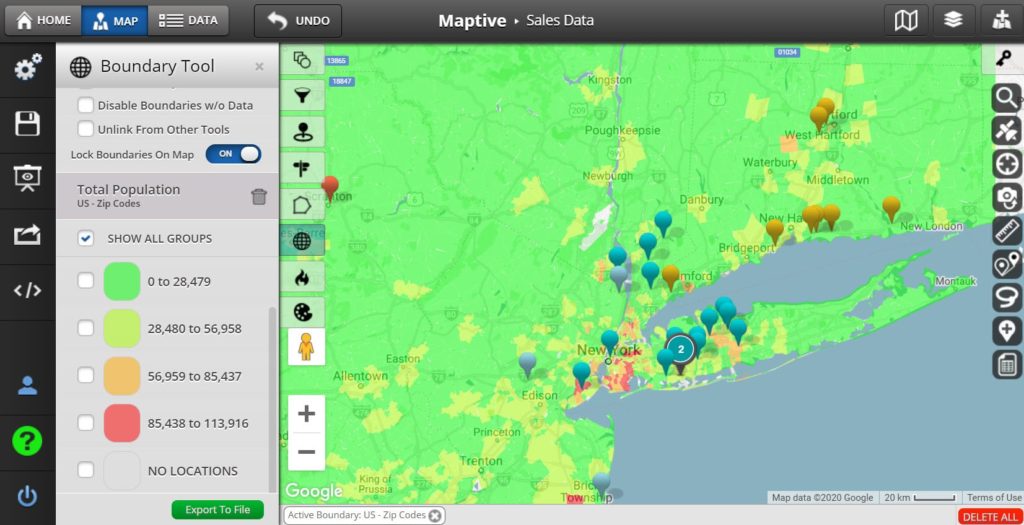
Choropleth maps use color variations to represent data values within predefined geographical regions. These types of map charts are ideal for showcasing regional variations, such as population density, election results, or income levels.
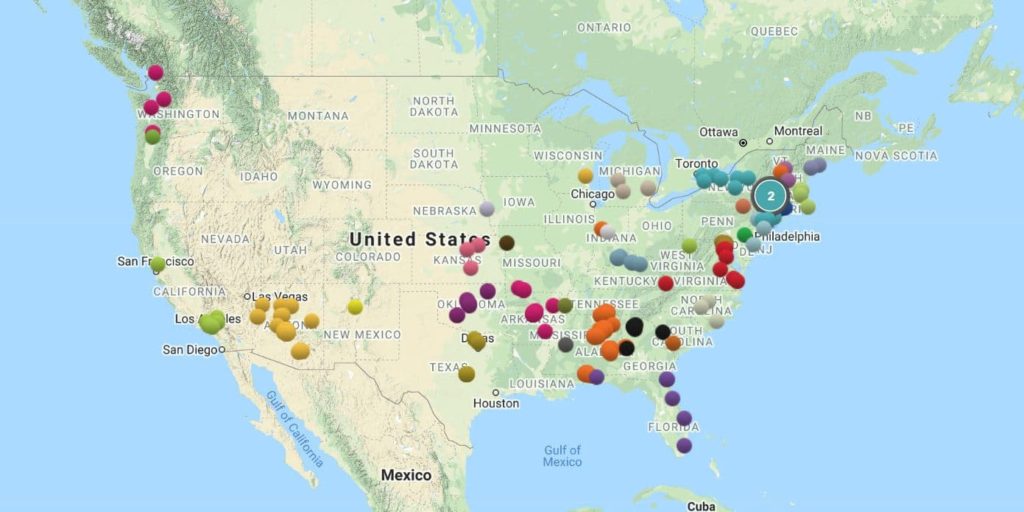
Point distribution maps pinpoint individual data points on a map, illustrating the location of specific events or objects. These map charts are great for visualizing the distribution of stores and customers.
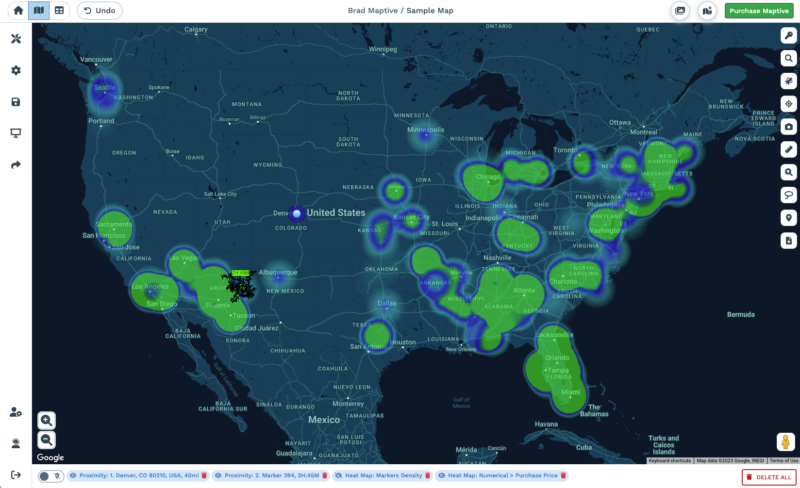
Heat Maps display the density of data values through color gradients. This type of map chart is really intuitive for viewers to understand and is often used to highlight the concentration of traffic hotspots, crime rates, or other critical data.
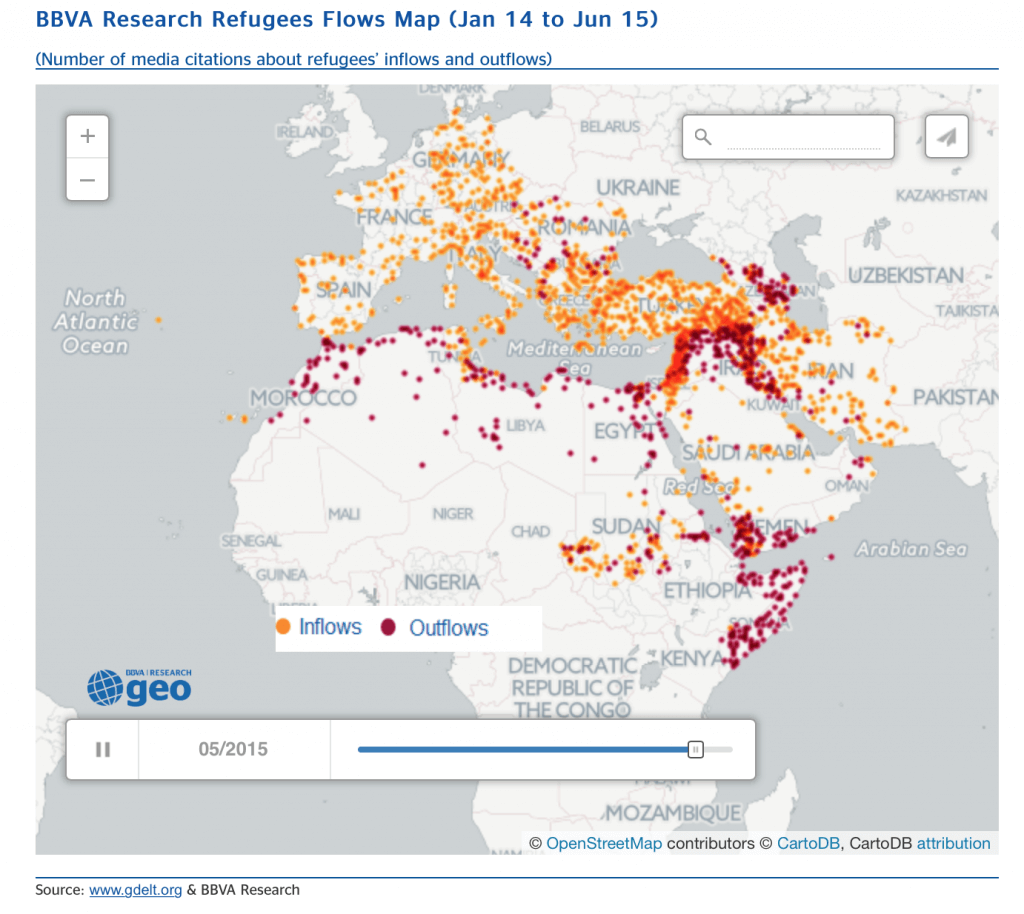
Flow maps visualize how objects or information move between locations. They are perfect for illustrating migration patterns, trade routes, or even communication networks.
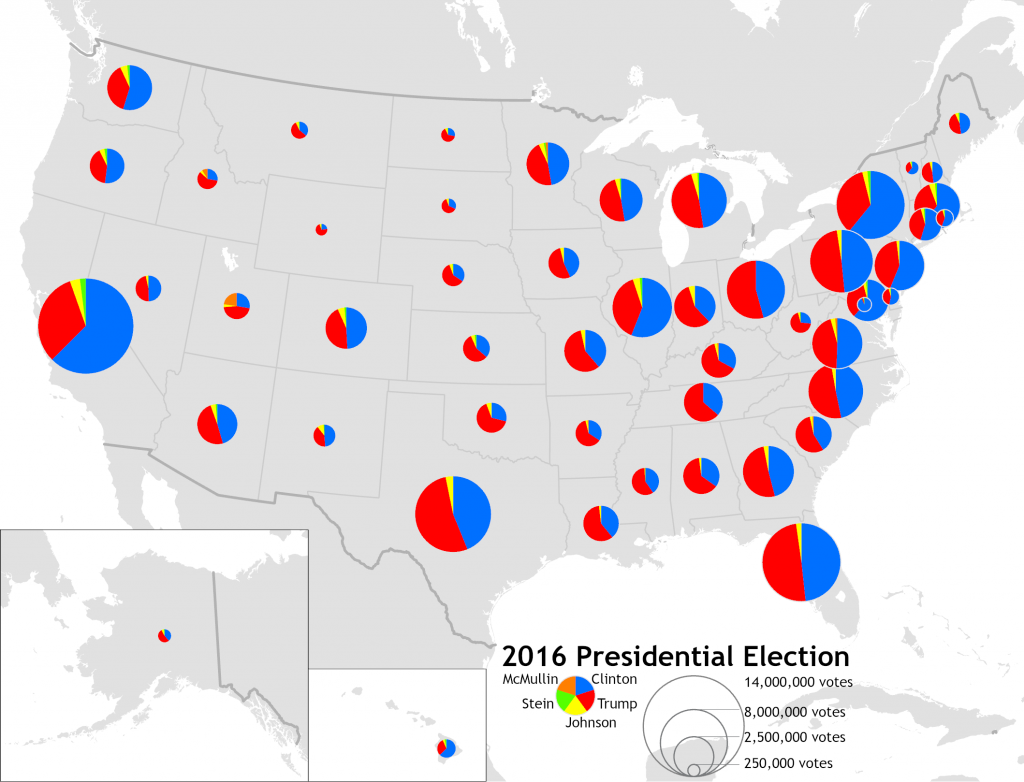
Proportional symbol maps use symbols of varying sizes to represent the quantity of a specific element in different locations. This type of map chart is useful for comparing data like sales volume or disease prevalence across regions.
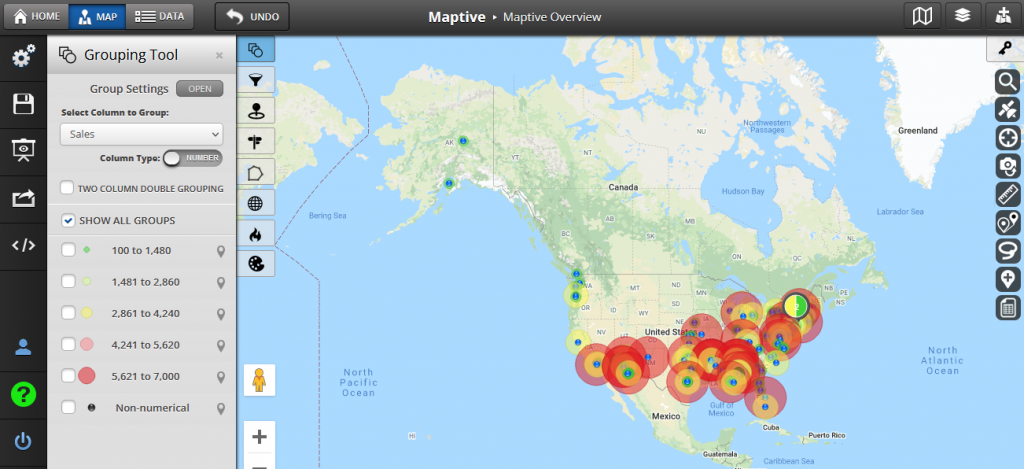
Bubble maps are a type of proportional symbol maps. In bubble maps, data points are represented not just by size but also by their precise locations on the map. This type of map can be used, for example, to evaluate production rates across different locations, where varying sizes of bubbles represent the scale and significance of manufacturing in each facility.
Beyond the map charts highlighted above, other variations and combinations exist, catering to specific data scenarios. As technology advances, more types of map charts are sure to be created to track market dynamics or analyze social trends. The adaptability of these types of visualizations ensures map charts remain at the forefront of data visualization.
We’ve already established that a map chart can convey a wealth of information while also displaying data in a topographical or spatial context. What else can a map chart do?
A map chart can benefit a wide range of users, depending on what they’re trying to visualize. Sales and marketing professionals often draw market distribution map charts to plan their targeting strategies, while business owners might create a market capacity map or use a map layer with geographical data to improve their supply chains.
Maptive’s intuitive interface makes creating a map chart very straightforward for users with various levels of expertise. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a map chart in Maptive:
We have not only answered the question “what is a map chart” but we have also established that they have become indispensable tools to visualize data within the context of geographic coordinates.
With their ability to communicate complex data patterns, compare information across regions, and identify clusters, map charts are essential tools for anyone looking to uncover new insights. As businesses and professionals navigate an era of increasing data complexity, embracing map charts can be the key to simplifying how socioeconomic data, critical indicators, sales revenue, and other specific metrics come alive on the world map.
Consider integrating these visualizations into your everyday business operations and you could unlock insights and transform data into actionable intelligence.
For those looking to embark on this journey, platforms like Maptive offer user-friendly solutions. Explore Maptive’s map chart functionality and leverage its resources for further learning. Embrace the transformative potential of map charts in your data storytelling, and chart a course toward more informed and impactful decision-making.
Brad Crisp is the CEO at Maptive.com, based in Denver, CO and born in San Francisco, CA. He has extensive experience in Business Mapping, GIS, Data Visualization, Mapping Data Analytics and all forms of software development. His career includes Software Development and Venture Capital dating back to 1998 at businesses like Maptive, GlobalMojo (now Giving Assistant), KPG Ventures, Loopnet, NextCard, and Banking.
